CHRNA2 receptor proteins may help fat cells burn energy
Posted: 22 May 2018 | Drug Target Review | No comments yet
The same proteins that moderate nicotine dependence in the brain may be involved in regulating metabolism by acting directly on certain types of fat cells…

The same proteins that moderate nicotine dependence in the brain may be involved in regulating metabolism by acting directly on certain types of fat cells, new research from the University of Michigan Life Sciences Institute shows.
Previous research by LSI research Assistant Professor Jun Wu and others identified a new type of fat cell in mice and humans, in addition to the white fat cells that store energy as lipids. These thermogenic, or “beige,” fat cells can be activated to burn energy through a process called thermogenesis.
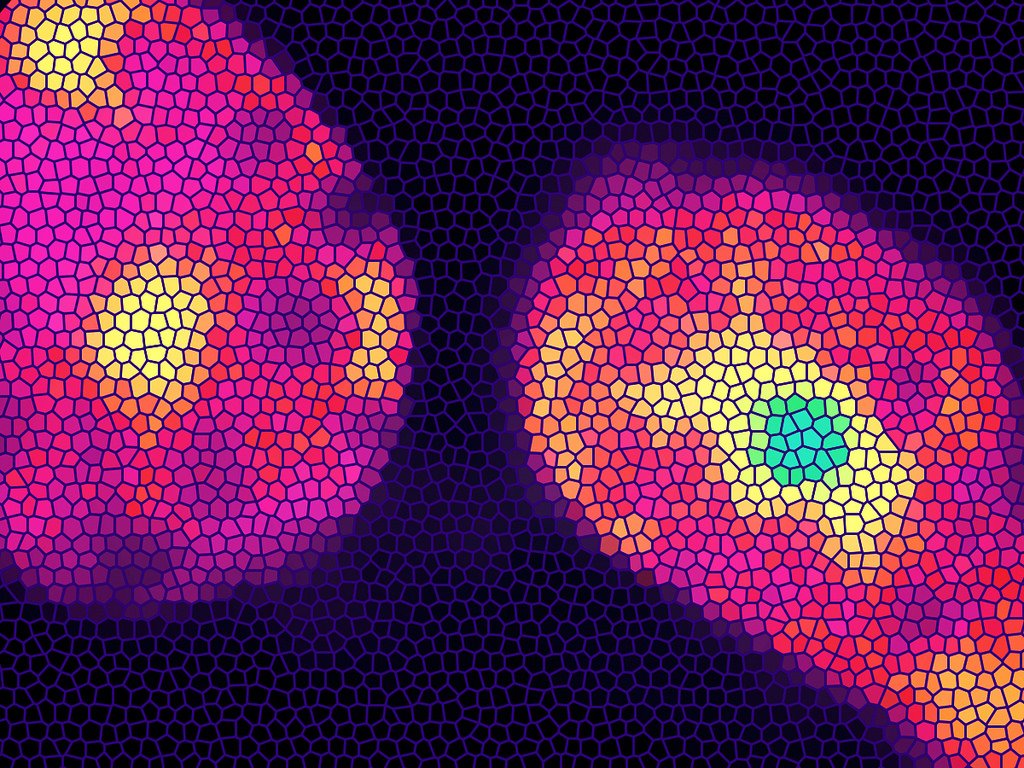

Illustration of thermogenesis in mice beige fat cells in response acetylcholine stimulation. (Stephanie King, LSI at University of Michigan)
To better understand what makes beige fat unique, Prof Wu and her colleagues analysed activated beige fat and uncovered a molecule directly linked to thermogenesis in these cells: CHRNA2 (for cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 2), a type of receptor that is best known for regulating nicotine dependence in brain cells.
Their findings reveal that CHRNA2 functions in mouse and human beige fat cells, but not in energy-storing white fat cells–indicating that this protein plays a role in energy metabolism.
This doesn’t mean that smoking is good for you, cautioned Prof Wu, but the findings may help further explain some of the weight gain that is associated with smoking cessation.
Research has shown that nicotine can suppress appetite. But by identifying how nicotine affects metabolism directly, this new study may open the door to more novel approaches to combating the weight gain that often occurs when individuals stop smoking.
In research conducted in human and mouse cells and in genetically modified mice, Prof Wu and her colleagues determined that CHRNA2 receptor proteins can be activated both by nicotine and by acetylcholine molecules produced by nearby immune cells. When the CHRNA2 protein receives the acetylcholine or nicotine, it stimulates the beige fat cells to start burning energy.
“It is really cool to discover a selective pathway for beige fat, a new cell type–and even more exciting that this is conserved in humans,” said Prof Wu, the study’s senior author and assistant professor of molecular and integrative physiology at the U-M Medical School.
To further test the role of CHRNA2 in metabolism, the researchers analysed mice that lacked the gene needed to make this protein.
“And the mice definitely are metabolically worse off, compared to the control group,” Prof Wu said.
Mice without the CHRNA2 gene showed no differences from the control group when they were fed a regular diet. But when they were switched to a high-fat diet, the mice lacking the gene exhibited greater weight gain, higher body fat content and higher levels of blood glucose and insulin–indicators of diabetes.
“Beige fat is very important in regulating whole-body metabolic health,” Prof Wu said. “Our results in mice show that if you lose even one aspect of this regulation–not the whole cell function, but just one part of its function–you will have a compromised response to metabolic challenges.”
Prof Wu believes that understanding the specific CHRNA2 signallingg pathway in beige fat also opens a new avenue for identifying druggable targets to treat obesity and metabolic syndrome.
“This pathway is important from a basic research standpoint, but it also has relevance for metabolic and human health research,” she said. “The more we can narrow down a precise pathway for activating beige fat, the more likely we are to find an effective therapy for metabolic health that does not carry harmful side effects.”
The research is published in Nature Medicine.
Related topics
Genomics, Protein, Proteomics, Therapeutics
Related organisations
University of Michigan Life Sciences Institute
Related people
Professor Jun Wu



