Gene therapy gives long-term protection to photoreceptor cells in retinitis pigmentosa model
Posted: 15 July 2015 | Victoria White
Scientists have shown that gene therapy can give protection to the light-sensitive photoreceptor cells responsible for colour vision in retinitis pigmentosa…
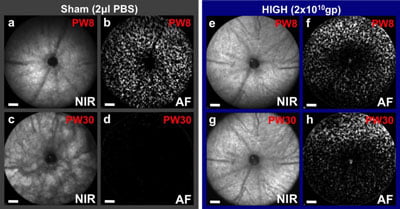

Prevention of retinal degeneration using CNTF gene therapy applied to one eye of a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa, which also has fluorescent cones that can be counted. At 8 weeks (PW8) both eyes appear similar, but by 30 weeks retinal pigment changes can be seen in the sham injected eye (c) as the degeneration progresses with all cones lost (d). In contrast, the CNTF treated eye (g, h) has a virtually unchanged fundal appearance and over 50% of cones surviving (from Lipinski et al., 2015). CREDIT: ©University of Oxford
Scientists have shown that gene therapy can give life-long protection to the light-sensitive photoreceptor cells responsible for colour vision in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa.
Results demonstrate that the preserved cells were able to drive visually-guided behaviour, even in later stages of the condition and despite becoming less sensitive to light.
These findings are significant because they open up a new line of research to prevent nerve cell death in retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration. They may also have a wider application to neurodegenerative disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
The research was led by Professor Robert MacLaren at the University of Oxford‘s Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology.
Retinitis pigmentosa affects 1 in 4000 people, with symptoms that typically appear between age 10 and 30. Night vision and peripheral vision go first, as the photoreceptors active in low light – the ‘rods’ – start to degenerate. Eventually the condition affects the ‘cones’ – the photoreceptors responsible for central, detailed, colour vision.
The current study looked at a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa in which the mice lack rhodopsin – the main pigment in rod photoreceptors. At age 4 weeks – after rod degeneration was underway and before cones were affected – the mice were dosed with a virus modified to produce human ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) protein in the retina.
CNTF is a compound previously shown to prevent the loss of photoreceptors and retinal ganglion cells. However its use as a potential treatment has been in question because of concerns about toxicity. The unique approach in this study was to use a mouse which had fluorescent green cone photoreceptors which could be counted by examining the living retina with a modified ophthalmoscope at various timepoints during the course of the degeneration. This allowed precise titration of the gene therapy dose which minimised any toxic effects.
Treatment was given to one eye, while saline was given to the other eye as a control. At 8 weeks, non-invasive imaging showed similar numbers of cones in all treated and untreated eyes. However, the number of cones decreased rapidly over the time course of the experiment in low-dose and control eyes, reaching 0 by week 24.
Preserved cones were shown to be functional using behavioural tests and imaging blood flow in the visual cortex
In contrast to previous CNTF studies, the research team was able to show that the preserved cones were functional by using behavioural tests and imaging blood flow in the visual cortex.
Next-generation sequencing at 30 weeks revealed that a group of genes previously linked to retinal disease were up to 89 times more active in high-dose eyes than in controls. Several genes usually active in the retina were also found to be less active in both medium- and high-dose eyes.
“Our results in this mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa clearly show that CNTF treatment can both give life-long protection to cone photoreceptors and preserve useful vision. While there remains a lot to understand, for example on the role of rods in cone preservation and translation to human retinal anatomy, this is a very promising study,” said MacLaren, Professor of Ophthalmology at the Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology.
“We already know from clinical trials aimed at preventing motor neuron loss in ALS that high-dose systemic treatment with CNTF causes too many adverse reactions to be tolerated by patients. However, our results suggest that directly increasing activity in the class of genes that were upregulated in our high-dose CNTF group has the potential to provide a novel, targeted treatment for retinitis pigmentosa and a range of neurodegenerative diseases.”
The study findings are published in the journal Molecular Therapy.
Related topics
Gene Therapy, Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Related conditions
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Related organisations
Oxford University



