Novel form of cell-free therapy revealed by researchers
Posted: 16 January 2020 | Victoria Rees (Drug Target Review) | No comments yet
Researchers have developed cytochalasin B-induced membrane vesicles which they suggest could be a new form of cell-free therapy in regenerative medicine.

Work on extracellular microvesicles (ECMVs) derived from human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has revealed a potential new form of cell-free therapy.
ECMVs are microstructures surrounded by a cytoplasm membrane; they have proven to be a prospective therapeutic tool in regenerative medicine due to their biocompatibility, miniature size, safety and regenerative properties. These can be used to circumvent the limitations of existing cell therapies without losing any effectiveness.
Cell therapies are grafts or implants of living tissue, such as bone marrow transplants, used to replace and regenerate damaged organ tissue. They currently have limited applications, as they work differently dependent on conditions and the environment they are placed into. They can also be rejected by the immune system.
A study at Kazan Federal University, Russia, has investigated cytochalasin B-induced membrane vesicles (CIMVs) which are also derived from MSCs and are very similar to natural ECMVs.
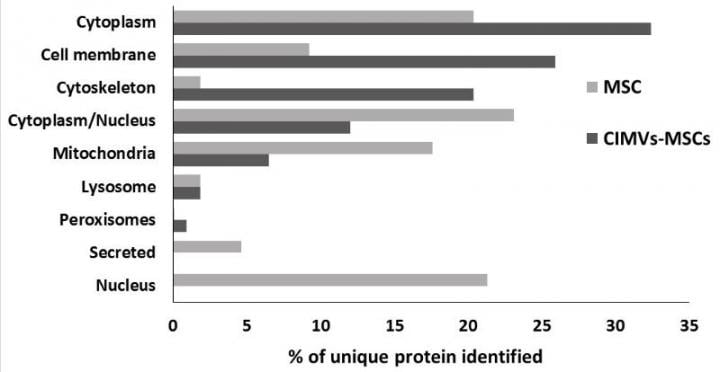

Proteome analysis of human MSCs and CIMVs-MSCs. Venn diagram of identified proteins MSCs and CIMVs-MSCs (A). Distribution of the identified proteins in organelles, percent of unique identified proteins (B) (credit: Kazan Federal University).
The scientists studied and characterised the biological activity of MSC-derived CIMVs. A number of biologically active molecules were found in CIMVs, such as growth factors, cytokines and chemokines; their immunophenotype was also classified. They also found that CIMVs could stimulate angiogenesis in the same way as stem cells.
The team came to the conclusion that human CIMVs-MSCs can be used for cell-free therapy of degenerative diseases. Induction of therapeutic angiogenesis is necessary for the treatment of ischemic tissue damage (eg, ischemic heart disease, hind limb ischemia, diabetic angiopathies and trophic ulcers) and neurodegenerative diseases (eg, multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), as well as therapies for damage of peripheral nerves and spinal cord injury.
The group say they are continuing to research the therapeutic potential for artificial microvesicles for autoimmune diseases.
The study was published in Cells.
Related topics
Cell Regeneration, Drug Targets, Regenerative Medicine, Stem Cells
Related conditions
Alzheimer’s disease, diabetic angiopathies, hind limb ischemia, ischemic heart disease, Multiple Sclerosis, trophic ulcers
Related organisations
Kazan Federal University



